Denver Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction/Sacroiliitis Specialists
What is it
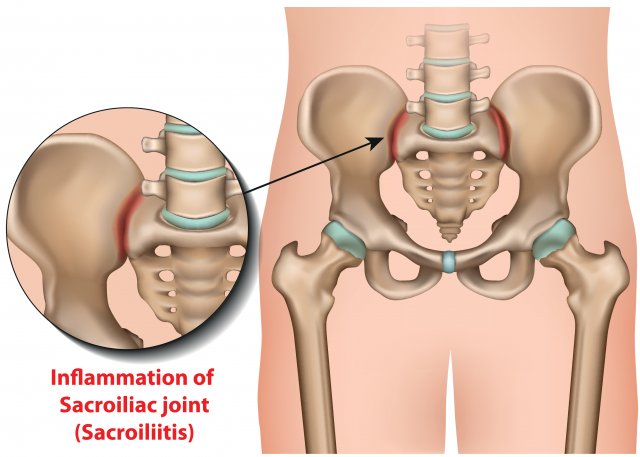
Sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction is pain stemming from the sacroiliac joint, which connects the iliac crests to the sacrum. SIJ dysfunction is often associated with either hypermobility or hypomobility of the joint. The SIJ is a 75% synovial joint with the remainder being fibrocartilaginous in nature. The superior aspect of the joint is often fused while the lower portion is more typical of a true synovial joint. It is innervated by lumbar and sacral dorsal rami (lumbar medial branch and sacral lateral branch nerves) as well as the lumbosacral plexus and superior gluteal nerves.
Diagnosis
SIJ dysfunction can be difficult to diagnose especially as it mimics other sources of pain. Typically, SIJ pain is described as low back and buttock pain as well as radiating pain into the upper leg and groin. Up to 30% of patients with low back pain actually have been found to have pain arising from the SIJ. Patients may report pain with position changes such as standing from a seated position or sitting on a hard surface. Relief with lying down or walking may be noted. There are many provocative maneuvers to help in the diagnosis such as FABER, Gaenslen’s, and thigh thrust tests. Overall these have shown to have a low sensitivity and specificity. Although Imaging modalities may be employed (radiographs, CT, MRI scans) in general these are not especially helpful as few abnormalities may be seen. Findings to look for include joint space narrowing and/or sclerosis of the SIJ. The most definitive evaluation is image guided injections of the SIJ with local anesthetic only. Greater than 75% relief would be diagnostic for SIJ dysfunction.
Treatment
Treatment starts with conservative care including physical therapy modalities and anti-inflammatory medications. Manipulative therapies have also been described. If these options fail, injections can not only provide diagnostic information but also therapeutic relief. Injection options include image guided SIJ intra-articular steroid injections and/or blocks of the L5 medial branch + sacral lateral branch nerves. If indicated radiofrequency ablation of these nerves can be done and provide longer term relief. Percutaneous SIJ fusion is also a new non-surgical option. Finally, if these modalities fail the next step would be evaluation for surgical treatment.
References:
Ou-Yang D, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2017:99:2027-36.
Zelle B, et al. Sacoiliac Joint Dysfunction. Evaluation and Management. Clinical Journal of Pain. Oct 2005;21(5):446-455.